Introduction To TSH Levels
Overview of TSH Levels
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is a critical component in the endocrine system, playing a pivotal role in regulating thyroid function.
Monitoring TSH levels is essential for diagnosing and managing various thyroid disorders, which affect millions of people worldwide.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about TSH levels, including their significance, how they are measured, and what different levels indicate about your thyroid health.
Importance of Monitoring TSH Levels
Regular monitoring of TSH levels can help detect thyroid dysfunction early, allowing for timely intervention and management. This is crucial as both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can lead to significant health issues if left untreated. Understanding your TSH levels can empower you to take control of your thyroid health and overall well-being.
What are TSH Levels?
Definition and Function
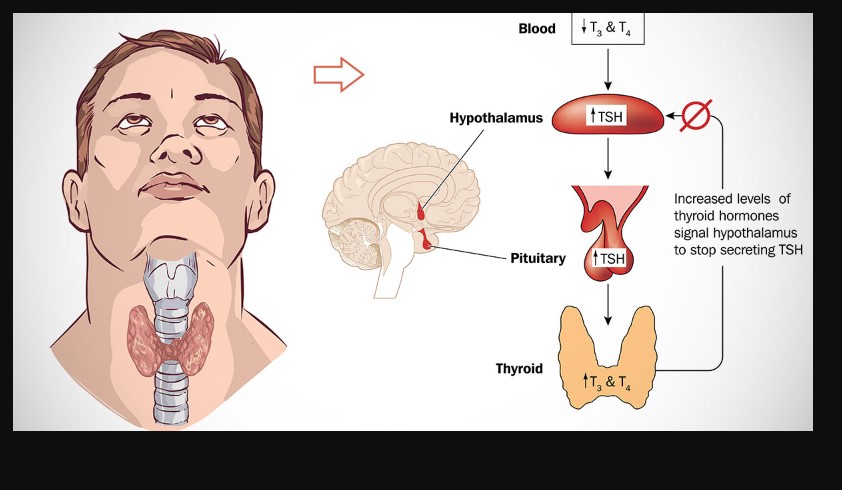
TSH, or thyroid-stimulating hormone, is produced by the pituitary gland and regulates the production of thyroid hormones, namely thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are vital for maintaining the body’s metabolism, energy levels, and overall metabolic health.
Role in Thyroid Health
TSH levels provide crucial insights into how well your thyroid is functioning. High TSH levels typically indicate an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), while low TSH levels suggest an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). By measuring TSH levels, healthcare providers can diagnose thyroid disorders and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
How TSH Levels are Measured
Blood Test Procedure
TSH levels are measured through a simple blood test. A healthcare provider will draw a small sample of blood, usually from a vein in your arm, which is then analyzed in a laboratory to determine the TSH concentration.
Interpreting TSH Test Results
The results of a TSH test are reported in milli-international units per liter (mIU/L). The normal range for TSH levels can vary slightly depending on the laboratory, but it generally falls between 0.4 and 4.0 mIU/L for adults. Results outside this range may indicate thyroid dysfunction and require further investigation.
Normal TSH Levels
TSH Range for Adults
For most adults, an average TSH level is typically between 0.4 and 4.0 mIU/L. However, optimal levels can vary based on individual factors such as age, health status, and laboratory reference ranges.
TSH Range for Children
TSH levels in children can differ from those in adults. For newborns, the range is usually higher, often between 1.0 and 39.0 mIU/L, gradually decreasing as they grow older. Pediatricians need to use age-specific reference ranges when evaluating TSH levels in children.
High TSH Levels
Causes of High TSH Levels
High TSH levels are often a sign of hypothyroidism, where the thyroid gland is not producing enough thyroid hormones. Causes can include autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, iodine deficiency, certain medications, and radiation therapy.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Common symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, hair loss, and constipation. If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to more severe complications such as heart disease, depression, and infertility.
Low TSH Levels
Causes of Low TSH Levels
Low TSH levels usually indicate hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. Causes can include Graves’ disease, thyroid nodules, excessive iodine intake, and thyroiditis.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism can include weight loss, heat intolerance, rapid heartbeat, nervousness, and tremors. Severe cases can lead to complications like atrial fibrillation and osteoporosis.
Factors Affecting TSH Levels
Medications
Certain medications can influence TSH levels, including thyroid hormone replacement therapy, antithyroid drugs, and medications containing iodine. Always inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy can significantly affect TSH levels due to increased hormone demands and physiological changes. Pregnant women often require closer monitoring of their thyroid function to ensure both maternal and fetal health.
Diet and Lifestyle
Dietary factors, such as iodine intake, and lifestyle habits, such as stress and sleep patterns, can also impact TSH levels. Maintaining a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle is crucial for optimal thyroid function.
Diagnosis and Tests for Thyroid Issues
Additional Thyroid Function Tests
Other thyroid function tests, including TSH tests, Free T4, Free T3, and thyroid antibody tests, help provide a comprehensive view of thyroid health and function.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies, such as thyroid ultrasound and radioactive iodine uptake tests, can evaluate the structure and activity of the thyroid gland and help identify nodules, goiters, and other abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Abnormal TSH Levels
Medications for Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is typically treated with levothyroxine, a synthetic thyroid hormone that replaces the deficient hormone. The dosage is adjusted based on regular monitoring of TSH levels.
Medications for Hyperthyroidism
Treatment for hyperthyroidism may include antithyroid medications like methimazole or propylthiouracil, which reduce thyroid hormone production. Beta-blockers may also be used to manage symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes for Thyroid Health
Dietary Recommendations
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients like iodine, selenium, and zinc is crucial for thyroid health. Foods such as fish, dairy, nuts, and whole grains can support thyroid function.
Exercise and Stress Management
Regular physical activity and stress management techniques, such as yoga and meditation, can positively impact thyroid health. Reducing stress helps regulate hormone levels and improve overall well-being.
Preventive Measures for Thyroid Disorders
Regular Screening
Regular screening for thyroid function, especially for individuals with a family history of thyroid disorders or other risk factors, can help detect issues early and initiate timely treatment.
Avoiding Risk Factors
Avoiding excessive iodine intake, radiation exposure, and certain environmental toxins can reduce the risk of developing thyroid disorders. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is also beneficial.
Personal Stories and Case Studies
Success Stories from Patients
Hearing from individuals who have successfully managed their thyroid disorders can be inspiring and informative. These personal stories highlight the impact of treatment and lifestyle changes on quality of life.
Impact of Treatment on Quality of Life
Effective treatment can significantly improve symptoms and overall health, allowing individuals to lead active, fulfilling lives. Monitoring and managing TSH levels is a critical component of this process.
Expert Insights on Thyroid Health
Quotes from Endocrinologists
“Regular monitoring of TSH levels is essential for diagnosing and managing thyroid disorders effectively. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve patient outcomes,” says Dr. John Smith, an endocrinologist.
Recent Research Findings
Recent studies have shown advancements in understanding the genetic and environmental factors influencing thyroid health, leading to more personalized and effective treatment approaches.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Monitoring TSH levels is vital for maintaining thyroid health and diagnosing thyroid disorders. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for abnormal TSH levels can empower individuals to take control of their health.
Encouragement for Regular Monitoring
Regular check-ups and proactive management of thyroid function can lead to better health outcomes. Consult with healthcare providers for personalized advice and stay informed about the latest research and treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is TSH?
TSH, or thyroid-stimulating hormone, regulates the production of thyroid hormones, which are crucial for metabolism and overall health.
How often should TSH levels be checked?
It varies depending on individual health conditions, but generally, TSH levels should be checked annually or as recommended by a healthcare provider.
Can diet affect TSH levels?
Yes, diet can influence TSH levels. Adequate intake of iodine and other nutrients is essential for maintaining healthy thyroid function.
What are the symptoms of abnormal TSH levels?
Symptoms of abnormal TSH levels include fatigue, weight changes, temperature sensitivity, and changes in heart rate.
How are thyroid disorders treated?
Treatment depends on whether the thyroid is overactive or underactive. It may include medications, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgery.